A business is an organized entity that operates to provide goods or services to customers in exchange for profit. Whether it’s a solo entrepreneur selling handmade crafts online or a multinational corporation like Apple, every business shares this fundamental purpose: creating value for customers while generating revenue for its owners.
Understanding what constitutes a business goes beyond this simple definition. Modern businesses operate within complex frameworks involving legal structures, regulatory requirements, and strategic planning. They must navigate everything from business licensing and registration to developing comprehensive business models that can adapt to changing market conditions.
This comprehensive guide explores the essential elements that define a business, from basic legal structures to advanced strategic frameworks. We’ll examine real-world examples, discuss the role of key business functions like business analysis and consulting, and provide practical insights for anyone looking to understand or start their own venture. For those interested in exploring how to start a business or discovering low-cost marketing ideas for startups, this foundation will prove invaluable.
Table of Contents
Core Business Structures: From Sole Proprietorship to Corporation
Every business must operate within a legal structure that defines its ownership, liability, and tax obligations. Understanding these structures is crucial for anyone asking “what is a business entity?” The choice of structure affects everything from daily operations to long-term growth potential.
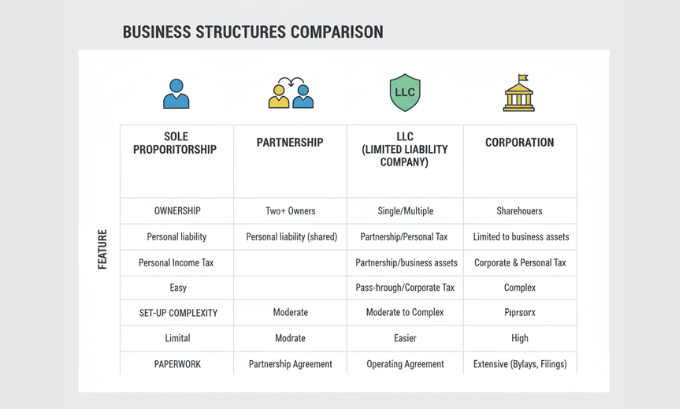
Sole Proprietorship: The Simple Start
A sole proprietorship represents the most basic business structure, where one individual owns and operates the entire enterprise. This structure requires minimal paperwork and offers complete operational control, making it attractive for freelancers, consultants, and small service providers.
The simplicity comes with trade-offs. Sole proprietors face unlimited personal liability, meaning their personal assets are at risk if the business encounters legal or financial difficulties. Additionally, raising capital can be challenging, as investors and lenders often prefer more formal business structures.
Partnerships: Shared Responsibility and Risk
Partnerships involve two or more individuals who agree to share ownership and operation of a business. General partnerships distribute profits, losses, and management responsibilities equally among partners, unless otherwise specified in a partnership agreement.
Limited partnerships offer an alternative structure where some partners (limited partners) contribute capital but don’t participate in daily management, while general partners handle operations and bear unlimited liability.
Limited Liability Companies: Flexibility Meets Protection
LLCs combine the liability protection of corporations with the tax benefits and operational flexibility of partnerships. This hybrid structure has become increasingly popular among small to medium-sized businesses because it protects personal assets while allowing for flexible management structures.
The LLC structure accommodates various ownership arrangements and provides significant flexibility in profit distribution and management roles. This makes it particularly suitable for businesses seeking to scale a business successfully while maintaining operational agility.
Corporations: Complex but Powerful
Corporations represent the most complex business structure, creating separate legal entities distinct from their owners. This separation provides the strongest liability protection but comes with increased regulatory requirements and potential double taxation.
C-corporations face double taxation—the corporation pays taxes on profits, and shareholders pay taxes on dividends. S-corporations avoid this issue by passing profits and losses directly to shareholders’ personal tax returns, but face restrictions on ownership structure.
| Business Structure | Liability Protection | Tax Treatment | Management Complexity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorship | None | Pass-through | Minimal | Individual professionals |
| Partnership | Limited | Pass-through | Moderate | Professional services |
| LLC | Strong | Flexible | Moderate | Most small businesses |
| Corporation | Strongest | Double/Pass-through | High | Growth-oriented companies |
The Business Planning Framework: Strategy Meets Execution
Every successful business begins with a solid plan that answers fundamental questions about market opportunity, competitive advantage, and financial viability. A business plan serves as both a roadmap for entrepreneurs and a communication tool for investors and stakeholders.

Core Components of Effective Business Plans
A comprehensive business plan typically includes an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organizational structure, product or service descriptions, marketing strategies, and detailed financial projections. Each section serves a specific purpose in demonstrating the venture’s viability and potential for success.
Market analysis represents perhaps the most critical component, requiring entrepreneurs to understand their target customers, competitive landscape, and industry trends. This analysis directly informs product development, pricing strategies, and marketing approaches.
For entrepreneurs exploring opportunities in digital commerce, understanding best e-commerce business ideas for beginners can provide valuable insights into market opportunities and business model variations.
The Role of Business Consultants in Strategic Planning
Business consultants provide external expertise to help companies develop strategies, solve problems, and improve performance. They bring industry knowledge, analytical skills, and objective perspectives that internal teams may lack.
Consultants often specialize in specific areas such as marketing, operations, finance, or technology. Their value lies in their ability to quickly assess situations, identify opportunities for improvement, and implement proven solutions. For companies seeking rapid growth, consultants can provide crucial guidance on scaling operations and entering new markets.
If you want to learn more about business consulting strategies, you may visit these comprehensive resources on digital transformation strategies that offer insights into modernizing business operations.
Business Analysis: The Bridge Between Strategy and Implementation
Business analysts serve as crucial intermediaries between business stakeholders and technical teams, ensuring that strategic objectives translate into practical solutions. They analyze processes, identify inefficiencies, and recommend improvements that align with business goals.
The role involves gathering requirements, documenting processes, and facilitating communication between different departments. Business analysts must understand both business operations and technical capabilities to propose realistic solutions that create measurable value.
Understanding Business Licenses and Registration Requirements
Operating legally requires proper licensing and registration, which varies significantly based on business type, location, and industry. These requirements exist to protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and generate tax revenue for government services.
The Business Registration Process
Business registration typically begins with choosing and reserving a business name, followed by filing appropriate formation documents with state authorities. The specific requirements depend on the chosen business structure and operating location.
Most states require businesses to obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS, even for single-owner businesses planning to hire employees or open business bank accounts. This number serves as the business equivalent of a Social Security number for tax purposes.
Industry-Specific Licensing Requirements
Many industries require specialized licenses or permits beyond basic business registration. Restaurants need food service licenses, construction companies require contractor licenses, and financial services firms must comply with securities regulations.
Professional services often require individual licensing as well as business permits. Doctors, lawyers, accountants, and engineers must maintain professional credentials in addition to business licenses.
For businesses looking to expand their reach through digital marketing, exploring digital marketing strategies can provide valuable insights into compliant promotional practices across different industries.
Business Models and Revenue Generation
Understanding different business models helps entrepreneurs choose approaches that align with their strengths, market opportunities, and growth objectives. Modern businesses often combine multiple revenue streams to create more stable and scalable operations.
Traditional Business Models
Product-based businesses generate revenue by manufacturing or sourcing physical goods for resale. This model requires inventory management, supply chain coordination, and often significant upfront capital investment.
Service-based businesses monetize expertise, labor, or specialized capabilities. These businesses typically have lower startup costs but may face scalability challenges since revenue often correlates directly with time investment.
Digital Age Business Models
Subscription models create recurring revenue by providing ongoing value to customers. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies exemplify this approach, charging monthly or annual fees for continued access to their platforms.
Platform businesses facilitate transactions between different user groups, typically earning revenue through transaction fees or advertising. Companies like Amazon FBA enable entrepreneurs to leverage established platforms while building their own businesses. For those interested in this approach, resources on Amazon FBA strategies provide detailed guidance.
Marketplace models connect buyers and sellers while taking a percentage of transactions. These businesses benefit from network effects—the platform becomes more valuable as more participants join.
Business Opportunity Assessment
Successful entrepreneurs develop systematic approaches to evaluating business opportunities. This involves analyzing market size, competition intensity, barrier to entry, and profit potential.
The Total Addressable Market (TAM) represents the total revenue opportunity available for a particular product or service. Understanding TAM helps entrepreneurs assess whether an opportunity justifies the required investment and effort.
Competitive analysis examines existing solutions, pricing models, and market positioning. This research identifies gaps in current offerings and opportunities for differentiation.
Business Operations and the Business Cycle
Understanding business operations requires recognizing how companies function within broader economic cycles and adapt to changing market conditions. Successful businesses develop resilient operations that can navigate various phases of economic activity.
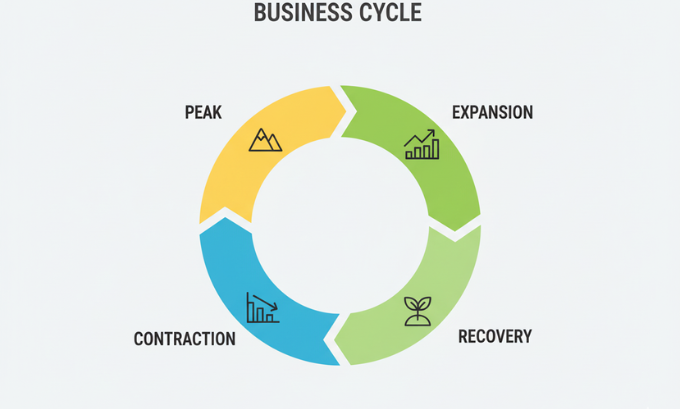
The Business Cycle’s Impact on Operations
The business cycle encompasses periods of expansion, peak performance, contraction, and recovery that affect all businesses to varying degrees. Companies must adapt their strategies, inventory levels, and workforce planning to align with these cyclical changes.
During expansion phases, businesses often focus on growth initiatives, hiring, and capacity expansion. Peak periods require careful inventory management and service delivery optimization to meet high demand.
Contraction periods necessitate cost management, efficiency improvements, and sometimes difficult decisions about workforce and operations. Recovery phases present opportunities for strategic positioning as markets stabilize.
Business Day Operations and Scheduling
Most businesses operate on standard business days—Monday through Friday, excluding holidays—which affects everything from customer service availability to supply chain coordination. Understanding business day conventions is crucial for setting customer expectations and coordinating with partners.
Some businesses extend beyond traditional business days to capture additional market opportunities or serve customers in different time zones. This decision requires careful analysis of additional costs versus potential revenue benefits.
Credit and Financing Operations
A business line of credit provides flexible access to capital for operational needs, inventory purchases, or growth initiatives. Unlike traditional loans, credit lines allow businesses to borrow only what they need when they need it, paying interest only on the amount used.
Business loans provide lump-sum funding for specific purposes such as equipment purchases, real estate acquisition, or major expansion projects. These typically offer lower interest rates than credit lines but less flexibility in usage.
For businesses interested in leveraging technology for growth, understanding ERP solutions for small business can provide insights into operational efficiency improvements.
Building Business Cases and Proposals
Effective business communication requires the ability to create compelling cases for new initiatives, investments, or partnerships. Business cases and proposals serve as decision-making tools that present opportunities, risks, and expected returns in structured formats.
Components of Strong Business Cases
A business case typically includes a problem statement, proposed solution, cost-benefit analysis, implementation timeline, and risk assessment. The document should present clear rationale for why stakeholders should approve and fund the proposed initiative.
Financial projections must include realistic assumptions about costs, revenues, and timelines. Decision-makers need to understand not just the potential upside but also the resources required and risks involved.
Business Proposal Development
Business proposals present solutions to client problems or opportunities for partnership. Unlike business cases, which are internal documents, proposals are external communications designed to win contracts or establish relationships.
Successful proposals demonstrate deep understanding of client needs, propose realistic solutions, and clearly articulate value propositions. They must balance technical detail with accessible language that decision-makers can easily understand.
For businesses developing comprehensive growth strategies, exploring resources on how to scale a business successfully can provide valuable frameworks for proposal development and strategic planning.
Business Education and Professional Development
Understanding business fundamentals increasingly requires formal education or structured learning approaches. Business administration degrees and specialized certifications provide foundational knowledge and credibility for career advancement.
Business Administration Education
Business administration degrees cover broad areas including management, marketing, finance, operations, and strategy. These programs provide comprehensive understanding of how businesses function and prepare graduates for leadership roles across industries.
Modern business education increasingly emphasizes practical application through case studies, internships, and project-based learning. This approach helps students understand how theoretical concepts apply to real-world business challenges.
Specialized Business Education
Beyond general business education, many professionals pursue specialized knowledge in areas like digital marketing, supply chain management, or financial analysis. These specializations provide deeper expertise in specific business functions.
Professional certifications in areas like project management, digital marketing, or industry-specific skills help professionals demonstrate competency and stay current with evolving best practices.
If you want to explore comprehensive digital transformation approaches, you may visit resources on digital transformation strategies that provide insights into modernizing business operations and processes.
Business Continuity and Risk Management
Successful businesses develop comprehensive plans to address potential disruptions and maintain operations during challenging circumstances. Business continuity planning has become increasingly important as companies face diverse risks from natural disasters to cyber attacks.
Business Continuity Planning Fundamentals
A business continuity plan outlines procedures for maintaining essential operations during and after disruptive events. These plans identify critical business functions, assess potential risks, and establish protocols for response and recovery.
Effective continuity planning requires regular testing and updates to ensure procedures remain relevant and effective. Companies must consider various scenarios and develop flexible responses that can adapt to different types of disruptions.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to business operations. This includes financial risks, operational risks, regulatory risks, and strategic risks that could impact business performance.
Companies use various tools and frameworks to systematically evaluate risks and develop appropriate responses. Some risks can be avoided through careful planning, while others require mitigation strategies or insurance coverage.
For businesses exploring advanced operational management, understanding warehouse management software for small business can provide insights into systematic risk reduction and operational efficiency.
Trust Structures and Advanced Business Arrangements
Business trusts represent sophisticated legal structures that can provide tax advantages, asset protection, and flexible governance arrangements for complex business situations.
Understanding Business Trusts
A business trust is a legal entity where a trustee holds and manages assets for the benefit of beneficiaries. These structures can provide privacy, tax efficiency, and succession planning advantages for business owners.
Business trusts operate under specific legal frameworks that vary by jurisdiction. They typically involve trustee responsibilities, beneficiary rights, and governance structures that differ significantly from traditional corporate arrangements.
Applications of Trust Structures
Business trusts often serve estate planning purposes, allowing business owners to transfer ownership interests while maintaining operational control. They can also provide asset protection benefits and tax planning opportunities.
Family businesses frequently use trust structures to facilitate generational transitions while preserving family control and values. These arrangements require careful legal and tax planning to achieve desired outcomes.
Measuring Business Success and Performance
Effective business management requires systematic measurement of performance across multiple dimensions. Modern businesses use various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and make informed decisions.
Financial Performance Metrics
Revenue growth, profit margins, and return on investment represent fundamental measures of business success. These metrics provide insights into operational efficiency and market performance.
Cash flow management often proves more critical than profitability for business survival, particularly for growing companies that require significant working capital investment.
Operational Performance Indicators
Customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, and retention rates provide insights into business model effectiveness and long-term sustainability. These metrics help companies optimize their marketing and service delivery approaches.
Employee productivity, quality metrics, and customer satisfaction scores offer additional perspectives on operational performance and areas for improvement.
For businesses looking to optimize their financial performance, exploring Monarch Networth Capital can provide insights into investment and wealth management strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a business plan and a business case?
A business plan is a comprehensive document outlining how a business will operate and grow, typically used for starting new ventures or seeking investment. A business case is a specific document justifying a particular project or investment within an existing organization.
How long does it take to register a business?
Business registration timelines vary by state and business structure, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks. Online filing systems have streamlined the process, with many states offering expedited processing for additional fees.
What is a business registration number used for?
A business registration number serves as a unique identifier for legal and tax purposes. Government agencies, banks, suppliers, and customers use this number to verify business legitimacy and track business activities.
Do all businesses need a business license?
Most businesses require at least basic registration with state authorities, though specific licensing requirements vary by industry and location. Professional services, food establishments, and financial services typically require additional specialized licenses.
What is the difference between a business day and a calendar day?
Business days refer to Monday through Friday, excluding holidays, when most commercial operations occur. Calendar days include all days of the week. This distinction affects contract terms, payment processing, and service delivery schedules.
How do I determine what type of business entity is right for me?
The choice depends on factors including liability protection needs, tax considerations, ownership structure, and growth plans. Consulting with legal and accounting professionals is recommended for making this important decision.
What should be included in a business continuity plan?
A comprehensive business continuity plan should include risk assessments, essential function identification, emergency contacts, backup procedures, communication protocols, and recovery strategies. Regular testing and updates ensure plan effectiveness.
How does a business line of credit differ from a business loan?
A business line of credit provides flexible access to funds up to a predetermined limit, with interest charged only on amounts used. A business loan provides a lump sum with fixed repayment terms and typically lower interest rates.
Building Your Business Foundation
Understanding what constitutes a business provides the foundation for entrepreneurial success and professional growth. From choosing appropriate legal structures to developing comprehensive business plans, each decision shapes the trajectory of business development.
Modern businesses operate in increasingly complex environments that require sophisticated understanding of legal requirements, financial management, and strategic planning. Whether pursuing traditional business models or exploring innovative approaches like e-commerce and digital platforms, success depends on mastering fundamental business principles.
The journey from business concept to successful operation involves numerous decisions and challenges. By understanding core business structures, planning requirements, and operational considerations, entrepreneurs can build stronger foundations for long-term success.
Remember that business success rarely happens overnight. It requires consistent effort, continuous learning, and adaptive strategies that respond to changing market conditions. The businesses that thrive are those that combine solid foundational knowledge with flexibility and innovation in execution.


